Storage Migration Recommendations
With VMware Cloud Foundation (VCF) 9 many customers are evaluating storage migrations for a number of reasons.. In some cases new VSAN ReadyNode(™) hardware is being deployed to support the VCF 9 deployment. In other cases migrations to VMFS or NFS from RDMs or vVols are being planned. Lastly some bare metal database workloads are being migrated, and some cloud workloads are being repatriated to vSphere to leverage the full storage capabilities of VMware Cloud Foundation 9. In addition customers may be migrating from older vSAN Original Storage Architecture (OSA) clusters, to vSAN Express Storage Architecture. VMware Cloud Foundation 9 includes a number of rich storage capabilities that enable any application or modern workload to run at its best.
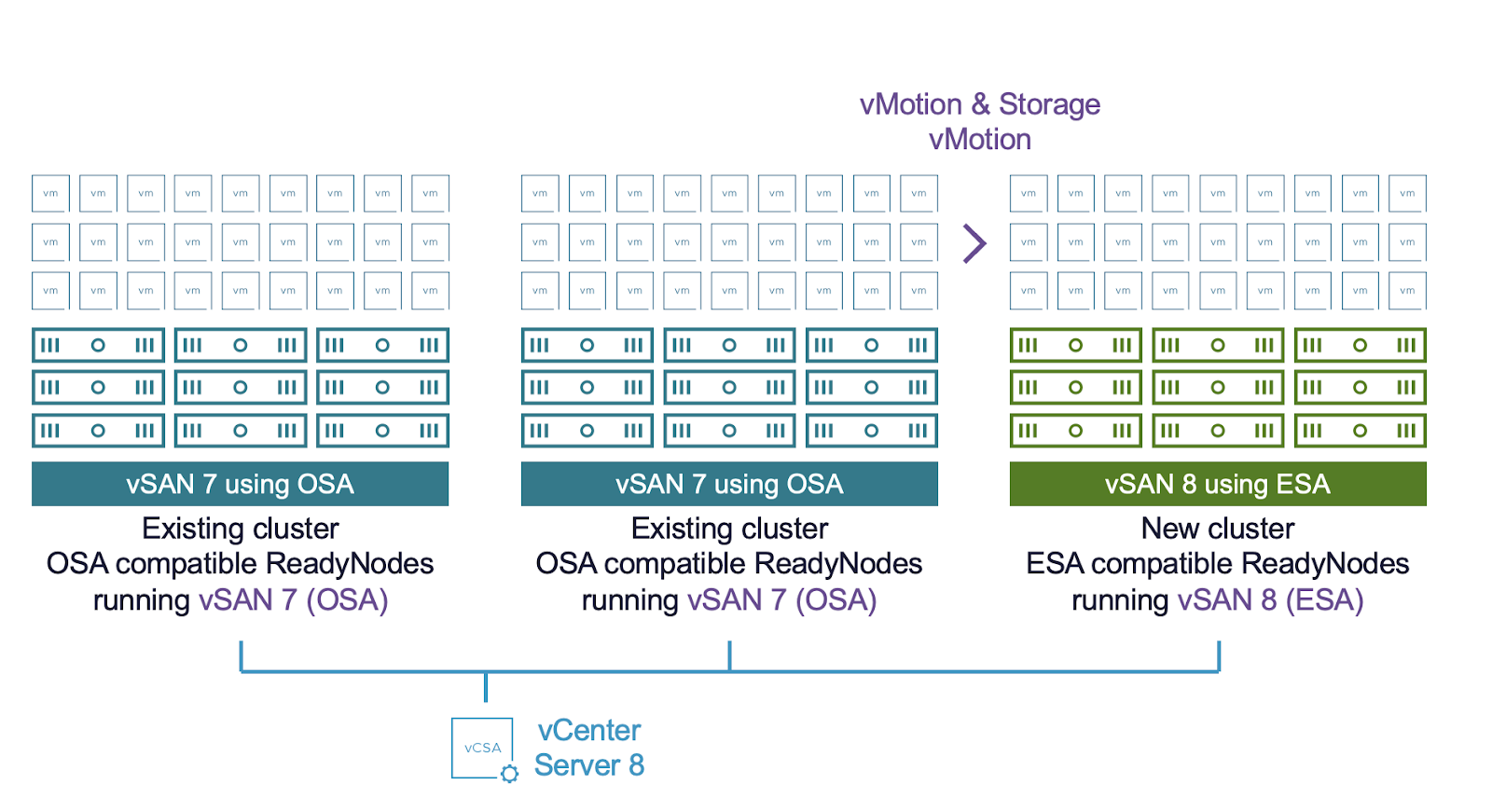
How do I migrate to VMware Cloud Foundation 9 storage?
Storage Migrations can be performed in a number of different ways. Migrations can be done from RDM to VMDK using the storage vMotion datamover. This can be done live for vRDMs and offline for pRDMs. Live Storage vMotion can be accomplished across all storage types (vSAN/vVols/VMFS/NFS), and can in addition cross cluster, and SSO boundaries (Shared Nothing vMotion).
For more detail on migration types and methods, see the Migration guide.
A number of other VMware tools ranging from HCX, to VMware Converter, and VLR can be leveraged to assist with cross cluster migrations and importing of workloads. A podcast covering a full range of migration options can also be found here.
VCF 9 Storage Services
Here is a non-exhaustive list of powerful storage capabilities exist to help support the most challenging workloads today:
Windows Server Failover Clustering (WSFC) is enabled on all VCF 9 storage platforms using clustered VMDK support. This eliminates the need for dedicated physical LUNs for WSFC and streamlines the process of setting up and managing clustered VMs.
Multi-writer Support shared disks enables Oracle RAC clusters to be supported on vSphere storage. This is supported on vSAN as well as on VMFS.
Large VMDK Support – VMDK’s up to 62TB are supported across all storage types, mirroring previous limits for vRDM and vVols.
Storage Policy Based Management (SPBM) – vSAN offers SPBM as a core operating model for storage management to allow VM centric storage management.
Container Storage Support – Kubernetes CSI Support allows for block storage to be automatically deployed for vSAN, VMFS and NFS. With VMFS and NFS you will need to use tags for the datastores. vSAN also supports using the CSI to provide NFS shares to containers.
Space Reclaim via UNMAP/TRIM from guest OS’s is supported across all VCF storage systems including NFS (new to VMware Cloud Foundation 9 via VAAI). For information about using this with VSAN see the vSAN space efficiencies guide.
Data at Rest and Data-In-Transit encryption – vSAN offers native data in transit encryption as well as transparent Data at Rest encryption. A native key manager is included in the vCenter server, so that 3rd party KMIP servers are not required to be deployed (but may optionally be used). Physical TPMs in hosts can also be used to help cache data at rest keys, as well as enable configuration encryption for the hosts. Encryption at rest and in transit for 3rd party storage can be enabled using VM Encryption. In addition NFSv4 now supports krb5p transit encryption as part of vSphere 9.
vTPMs – vTPMs are supported to expose a secure place to store secrets for virtual machines.
Thin provisioning – Is supported on all VMDKs, and should be seriously considered as a default for all vSAN/NFS/VMFS storage.
Compression and Deduplication – Is supported on vSAN, now with global deduplication.
Databases as a Service (DBaaS) – Optionally, Data Services Manager (DSM) 9 enables a number of database platforms (MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server). Being able to programmatically and automatically deploy database clusters, patch, maintain and back them up, and automate most database management functions is a powerful advanced service available to VMware Cloud Foundation 9.
Snapshot Support – vSAN Express Storage Architecture offers high performance snapshots that avoid stun performance impacts, and allow long term retention using vSAN data protection to automate schedules and immutable retention. In addition it can be complemented with VMware Live Recovery for vaulting of snapshots at a secondary cluster.
Disaster Recovery – VMware Live Recovery (Formerly SRM) allows for secure, efficient replication and orchestration of copies of virtual machines to secondary locations for rapid recovery in the event of a disaster recovery.
Asynchronous Replication – vSphere Replication enables asynchronous copies with snapshots recovery points to be kept at a secondary location.
Synchronous Replication – Both vSAN and a number of 3rd party storage platforms support synchronous replication for the purposes of building a stretched cluster.
vSphere Backup APIs (Formerly known as VADP) – A rich set of backup support allows for automatic, low impact changed block tracking based backups to be made. A number of modes are supported ranging from network mode, hot add mode, and direct SAN mode. In addition reverse changed block tracking restores are also supported.
vStorage APIs for Array Integration (VAAI) – A number of features exist for both VMFS and NFS to allow speciality integrations and offload. For more information about these capabilities see this FAQ.
vSphere APIs for IO Filtering (VAIO) – This allows a VM to have its IO safely and securely filtered in accordance with a policy. This is primarily used for near real time backup and replication. For information on supported platforms see this compatibility guide..
Conclusion
VMware Cloud Foundation is the leading private cloud platform today, and it offers the richest blend of storage services and 3rd party platform integration and support. As vSphere 7 reaches the end of general support this year, it is important to begin migration planning, as well as start evaluating the improvements that VMware Cloud Foundation 9 will offer vSphere 8 environments.



